SHARE
| Mar-23-2021
E-Invoice under GST
Contributed by CA. Manoj Mehta
In Common parlance the concept of E-invoicing (Electronic invoicing) is the exchange of the invoice document between a supplier and a buyer in an integrated electronic format. This is slightly different from the current Digital Invoice which is shared in a PDF/ Web or other formats. Infact traditional invoicing is heavily paper-based process and also manually intensive prone to human error resulting in increased costs and processing lifecycles for companies. Read on …
The true definition of an electronic invoice is that it should contain data from the supplier in a format that can be entered (integrated) into the buyer’s Account Payable (AP) system without requiring any data input from the buyer’s AP administrator other than Approval for posting. Each Country have defined a standard and adopted the same. Recent adoption in the Asia Country is by Singapore who has used Pan-European Public Procurement On-Line (PEPPOL) Standard. Globally accepted standard on e-Inovice, is Univeral Business Language (UBL). All these standards aim to having a common business language. These standards are aligned with the local laws by each country. After implementation of this standard all accounting application will generate same electronic version of the Invoice. In the current system India, each ERP has their database and the eVersion of the Invoice be it XML / JSON or any other format would have different header or nomenclature, which leaves no room for interoperability. The machine readability and uniform interpretation is the key objective of e-Invoice.
e-Invoice in India
In the 35th GST Council Meeting , the introduction of ‘E-invoicing’ or ‘Electronic invoicing’ has approved and planned in a phased manner for reporting of invoices to GST System before issuing to the customers. It was decided to start E-invoicing from 1st January, 2020, on voluntary basis and mandatory from 01st April, 2020. Since there is no standard for e-invoice, existing in the country, standard for the same has been finalised after consultation with trade/industry bodies as well as ICAI, after keeping the draft in public place.
implement E-invoicing
CBIC issued 5 notifications on 13th December 2019, bearing numbers 68/2019 – Central Tax to 70/2019 – Central Tax, to implement the provisions of E-invoicing. Notification No. 02/2020 – Central Tax has notified the Schema. Summary of these notifications are as follows.
- Registered person whose aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeds ` 100 Crores, shall prepare E-invoice and same will be mandatorily from 1st April 2020 for the all transactions except B2C transactions and Bill of Supply.
- New sub rule 4 has been introduced under Rule 48 under CGST Rules. As per this new rule, the invoice shall be prepared by including such particulars as contained in FORM GST INV-01, after obtaining an Invoice Reference Number (IRN) by uploading same information on the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
- As per the Scheme released by GSTN, the details of supplier, details of buyer and consignee, type of supply, details of supply (HSN Code, value, description, tax, etc), to be uploaded in the form of GST INV-01 on Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
- Taxpayers needs to obtain Invoice reference number by uploading the information on Invoice Registration portal.
- Invoice issued without Invoice reference number will be treated as Invalid invoice for the taxpayers whose turnover is more than 100 crores.
- Following are the common goods and service tax electronic portal for the uploading of E-invoice. www.einvoice1.gst.gov.in –to– www.einvoice10.gst.gov.in.
- In case of E-invoice, the provisions of the CGST Rule 48(1) and (2) are not applicable. The said sub rules are containing the provisions of issue of triplicate invoices and duplicate invoices in case of Goods and Services respectively.
- Timing of issue of invoice as mentioned in Section 31 of CGST Act, does not get changed due to the introduction of E-invoice. In other words, the time of generation of invoice in case of Goods will be, before or at the time of removal of goods / delivery of goods, etc. and before or after the provision of service in case of services as prescribed in Section 31(2) of the CGST Act.
Salient Features of E-Invoice
- E-invoice does not mean generation of invoices from a central portal of tax department.
- All accounting software are expected to adapt the new e-Invoice standard wherein they would re-align their data access and retrieval in the standard format.
- There would not be any change in the format and mode of delivery of invoice to the customer.
- Generation of e-invoice will be the responsibility of the taxpayer who will be required to report the same to Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) of GST, which in turn will generate a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN).
- E-Invoice is required to be issued in case of all types of supply including reverse charge, exports, Business to Government, etc., except B2C. In case of B2C, the QR code is must for the taxpayers whose total turnover is more than ` 500 crores in the financial year.
- E-invoicing is not merely limited to the issuance of invoices, but also extends to the credit notes, debit notes, etc.
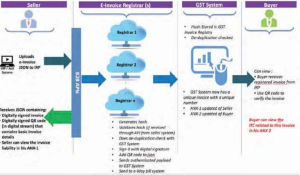
Workflow of E-invoice
The flow of the e-invoice generation, registration and receipt of confirmation can be logically divided into two major parts.
- The first part being the interaction between the Accounting Software and the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP).
- The second part is the interaction between the IRP and the GST/E-Way Bill Systems and the Buyer.
Process Flow
- Invoice will be generated from the accounting software.
- The invoice data must conform to the e-invoice schema (standards) that is published and have the mandatory and optional parameters.
- Details of the invoices need to be uploaded to the Invoice Registration portal.
- This activity can be done through Web based or also through API based. GSTN will also provide offline tool to serve this purpose. In case of volume of business, better to choose API mode. National Informatics Centre (NIC) has stated that there would be 6 differentAPIs. It has currently released specs for critical APIs (such as Generation).
- The Invoice Registration Portal (IRP) will generate the hash/ Invoice reference Number and ensure it is not duplicate in a particular year.
- IRP will add its signature on the invoices data as well as a the QR code.
- Invoice Registration Portal will send back signed JSON with IRN, back to taxpayer with a QR code. But it is optional for supplier to sign the JSON before submitting the e-invoicing details to IRP.
- The said Invoice reference number (IRN) should be printed on the invoice, to be issued by taxpayer to customers.
- The IRP will push the Invoice data to the GST System. The GST system will convert the e-invoice received and populate it into the GST ANX 1 and GST ANX 2 of the seller and buyer respectively.
- For e-way bill perspective, transporter ID parameter will be created in the e-invoice schema. Part A of the e-way bill will be populated from the e-invoice schema data itself.
- IRN shall also be required to be part of the invoice issued for all formal purposes.
Generation of e-invoice will be the responsibility of the taxpayer who will be required to report the same to Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)
Amendment/cancellation of e-invoice
- The e-invoice mechanism enables invoices to be cancelled. This will have to be reported to IRP within 24 hours. Any cancellation after 24 hours could not be possible on IRP; however, one can manually cancel the same on GST portal before filing the returns. Hence, cancellation beyond 24 hours are reconciliation item between Invoice Portal and GST portal and financials.
- Amendments to the e-invoice are allowed on GST portal as per provisions of GST law.September of next year is the last month to amend e-invoices in the GST portal for a particular financial year.
Challenges Ahead
Cost to businesses: The existing ERP system must be re-configured in view of requirement of seamlessly sync with IRP. It will have one- time cost, most as well recurring cost. A large group having different business verticals within the group, may have varying demands for invoice generation, which would require additional customisation of commonly maintained ERP systems Operational Challenges: The scheme issued for E-invoice is having many optional fields. Businesses will also have to look at the requirements for skill development and further upgradation for Staff concerned with invoice generation and accounts.
Additional technological upgradation can also be undertaken to automate processes such as payment, reconciliation with PO raised by buyer as well as bank statement to fully realise the benefits of the transition.
Way forward
The introduction of e-invoicing, promises to be the most significant step since the introduction of
the GST. The businesses must understand the proposed system at its very inception, so that adequate preparation can be taken care of.
In sum, this must be seen as a tax compliance tool evolved as a technological solution.
The data requirements as mentioned in the schema provided by GSTN, have to be understood thoroughly. This requires a high degree of standardisation of invoicing operations and will necessitate the involvement of various stakeholders including internal teams such as Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable as well as external players such as customers, suppliers, etc.
In sum, this must be seen as a tax compliance tool evolved as a technological solution. E-invoicing is conceptualised to be a win-win situation; with digitisation resulting in ease of compliance for business, as well as real-time access to data, to tax administrators.
Similar reads
The Hon’ble Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman, while presenting the Interim Budget 2024-25 in Parliament today asserted that by unifying the highly fragmented i
Read More
The Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) ushers in a transformative update to the GSTR-1 return, unveiling two pivotal tables – Table 14 and Table 15.
Read More
The latest release of TallyPrime is loaded with key features such as GST reconciliation ( GSTR-2A, GSTR-2B, and GSTR-1), multi-GSTIN support in a single company, powerful report filters, and..........
Read More
Key Recommendations of the 52nd GST Council Meeting: All You Need To Know 📌 A. Recommendations relating to GST rates on goods and services: 📢 I. Changes in GST rates of goods: ➡️ GST rates for "F
Read More
NIC has published the following error codes, error message, the reasons for the errors and the corresponding resolutions to help you resolve errors faced during e-Invoice upload to the NIC portal.
Read More


